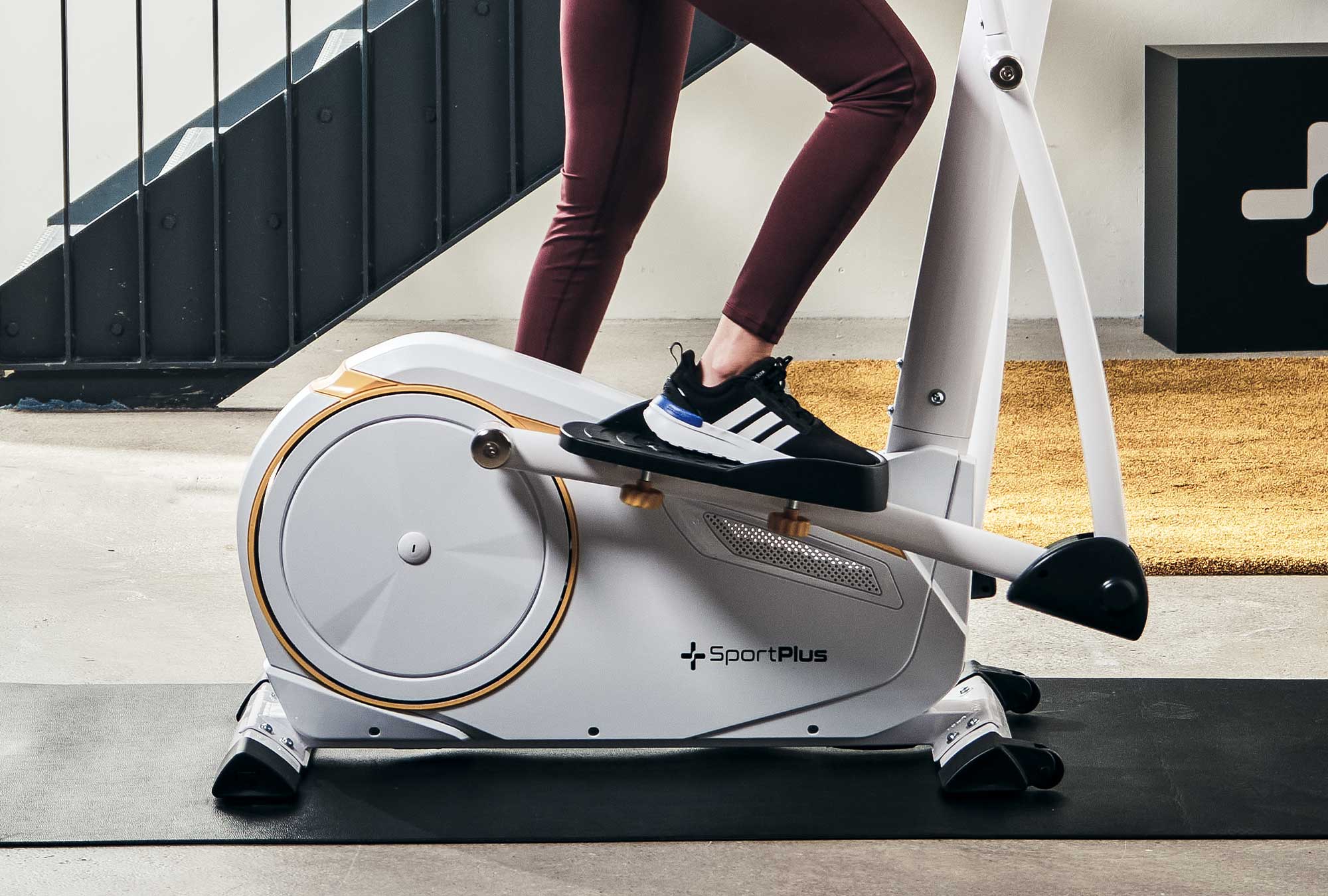
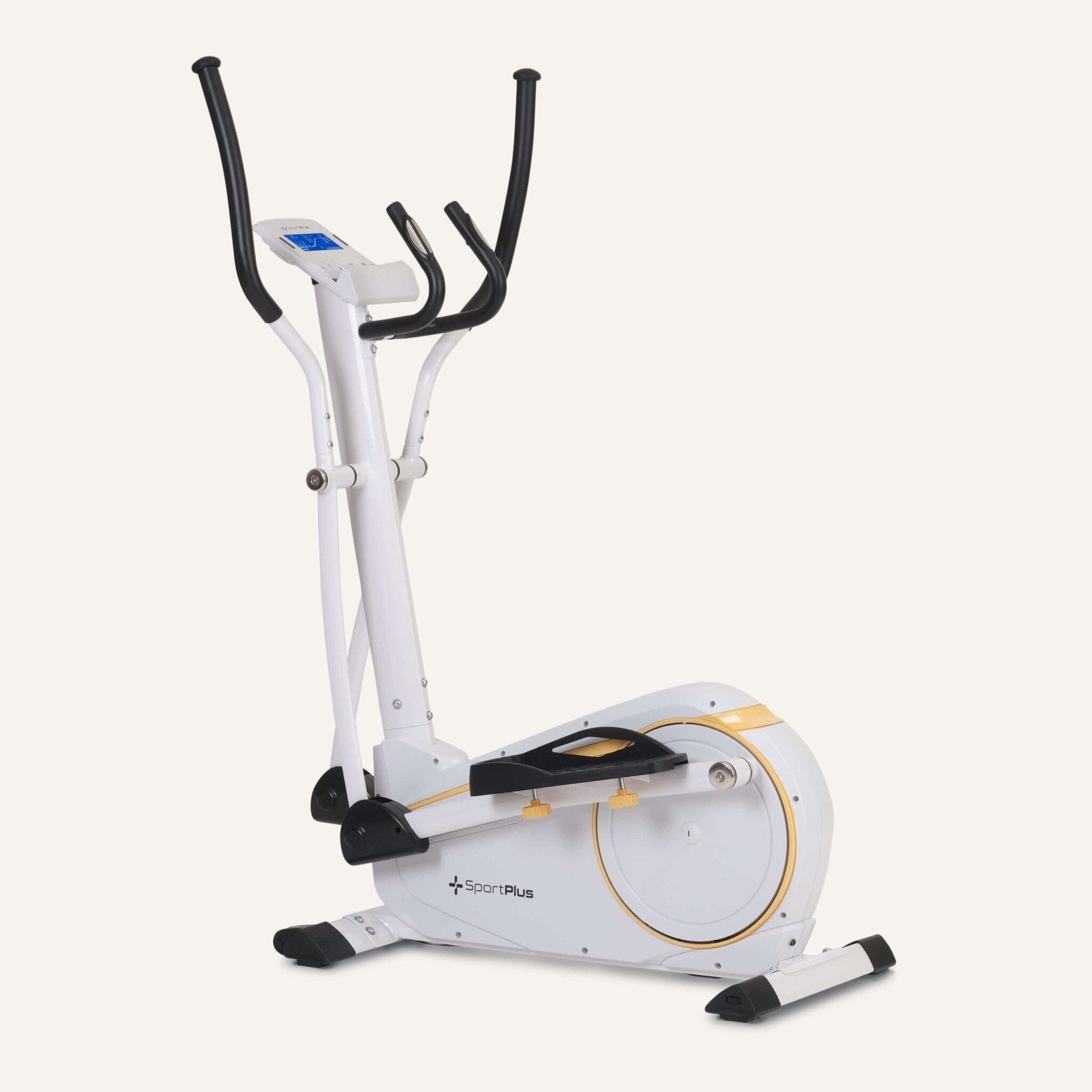
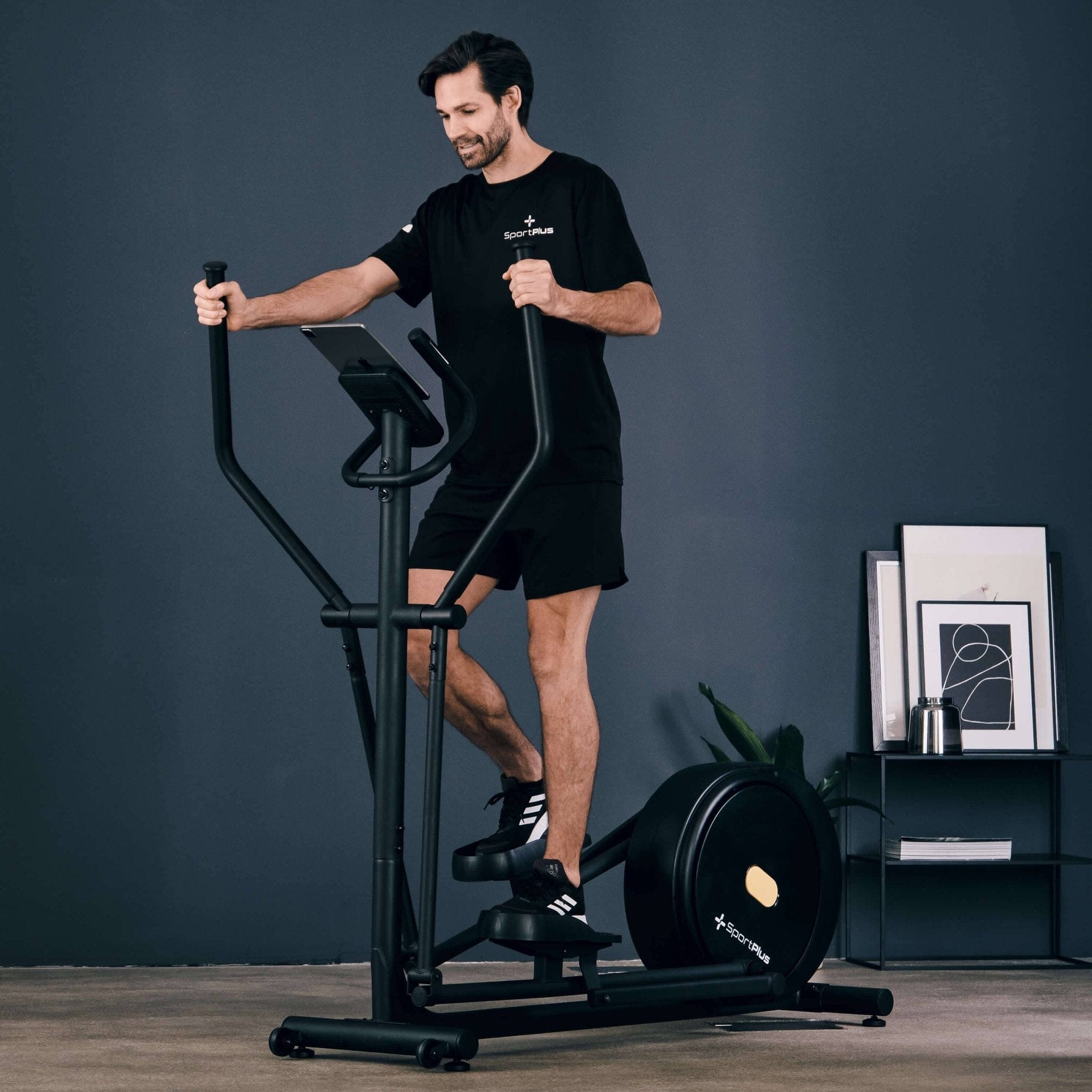
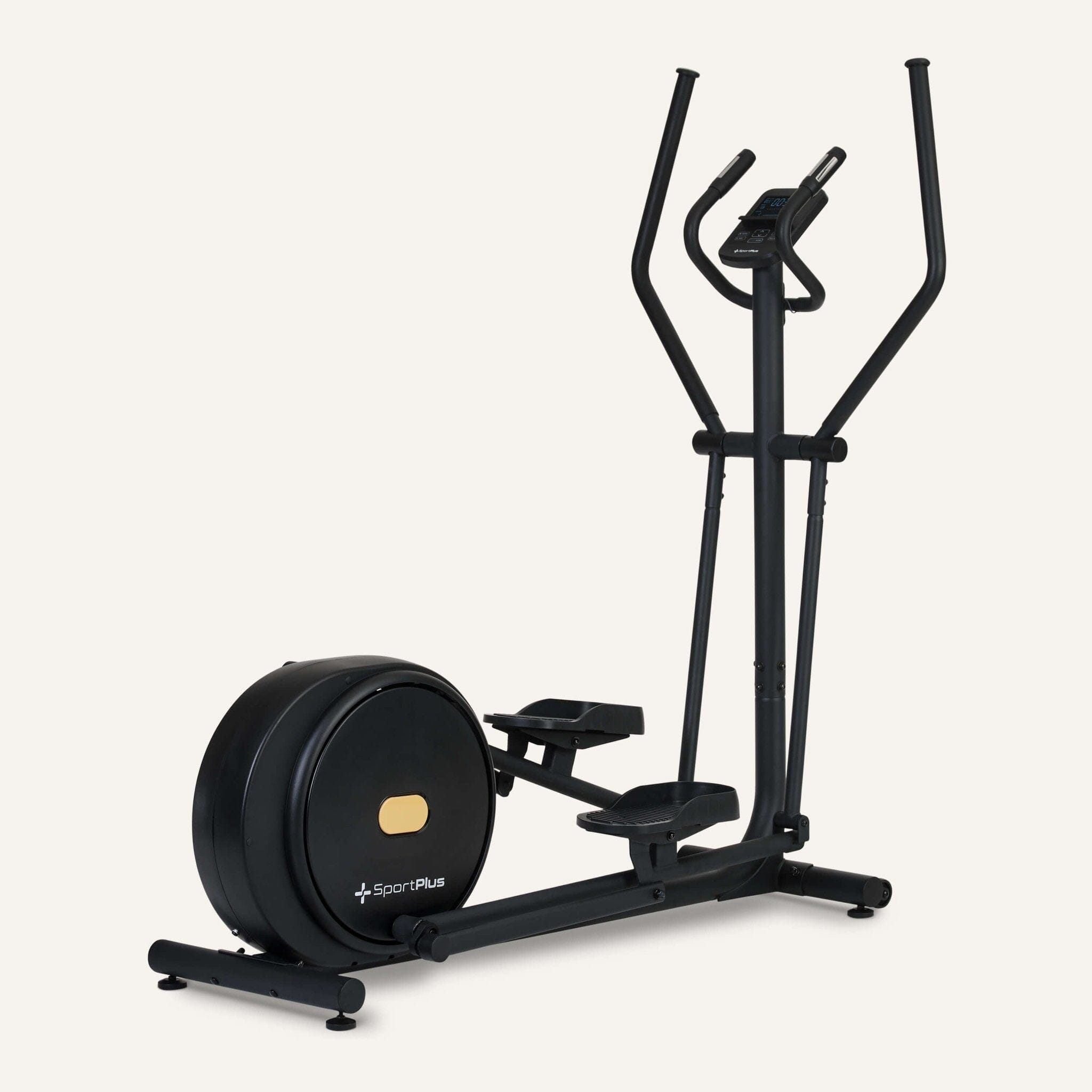
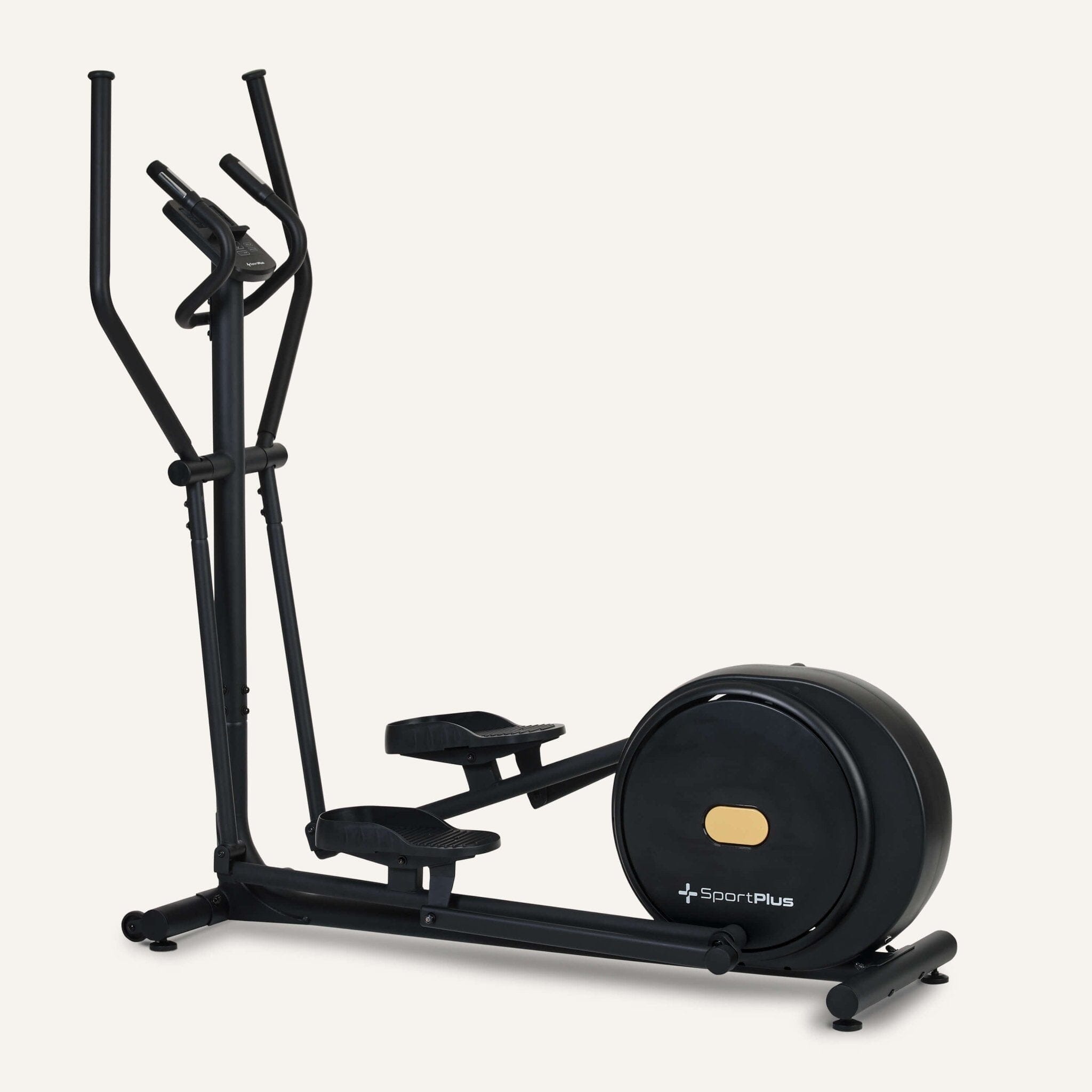
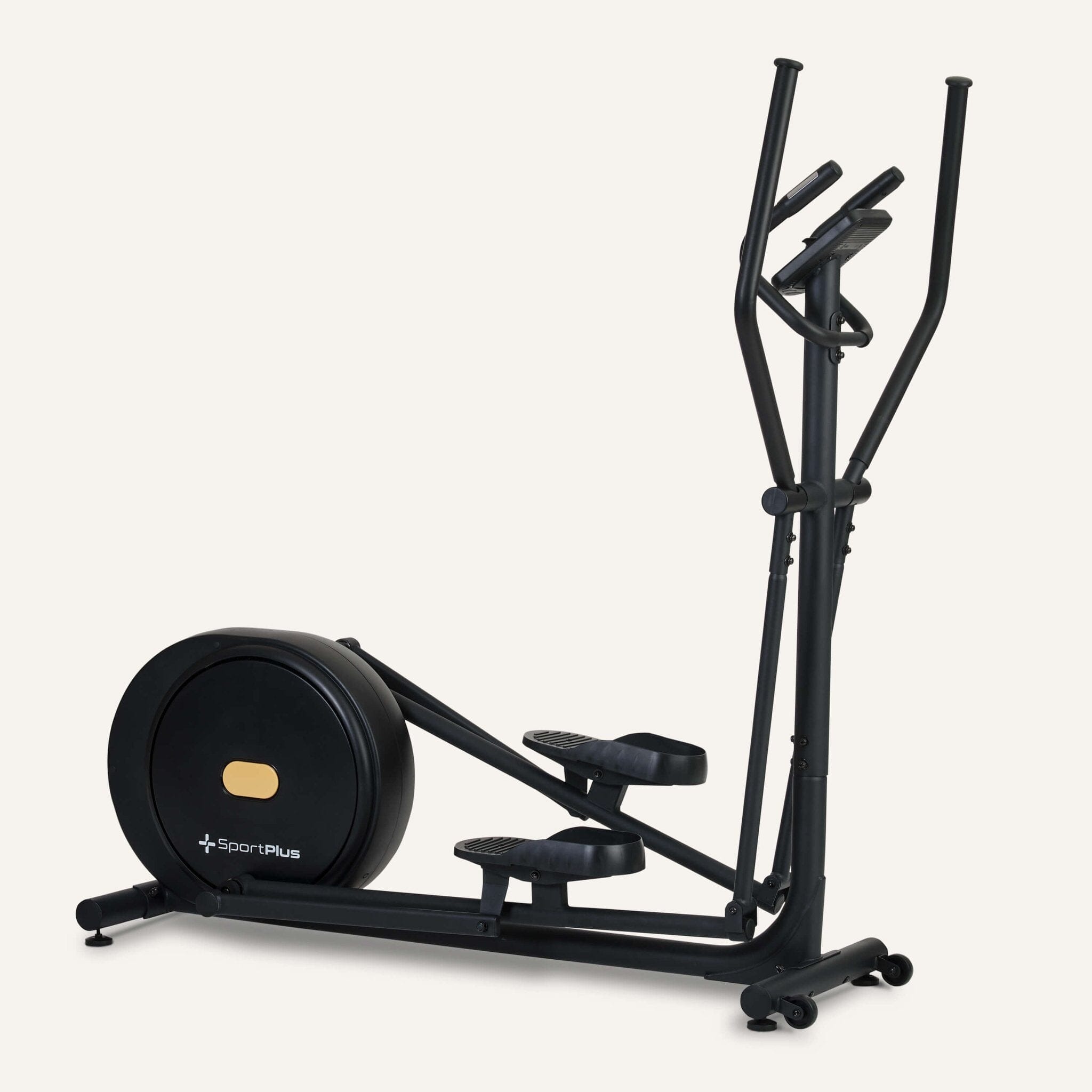
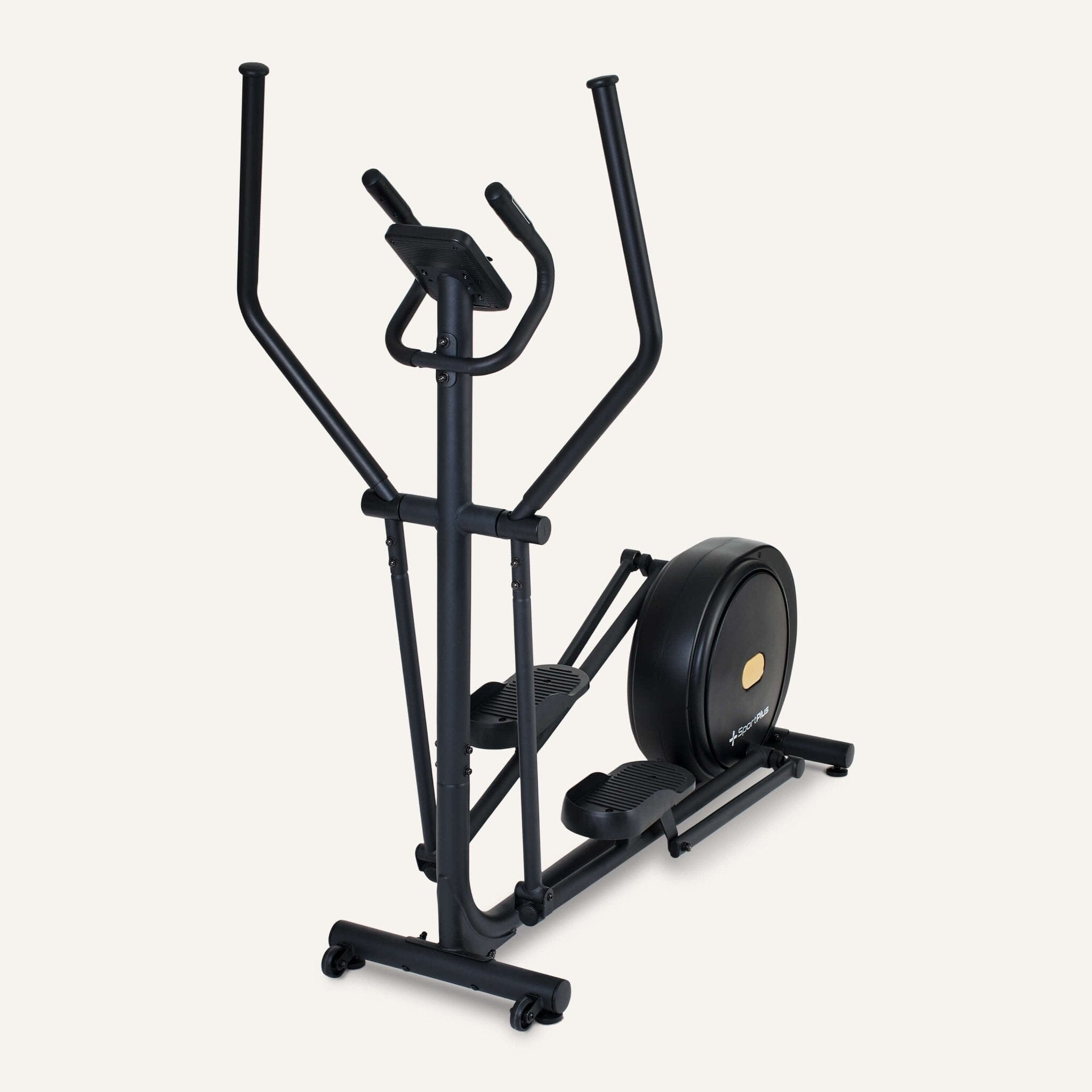
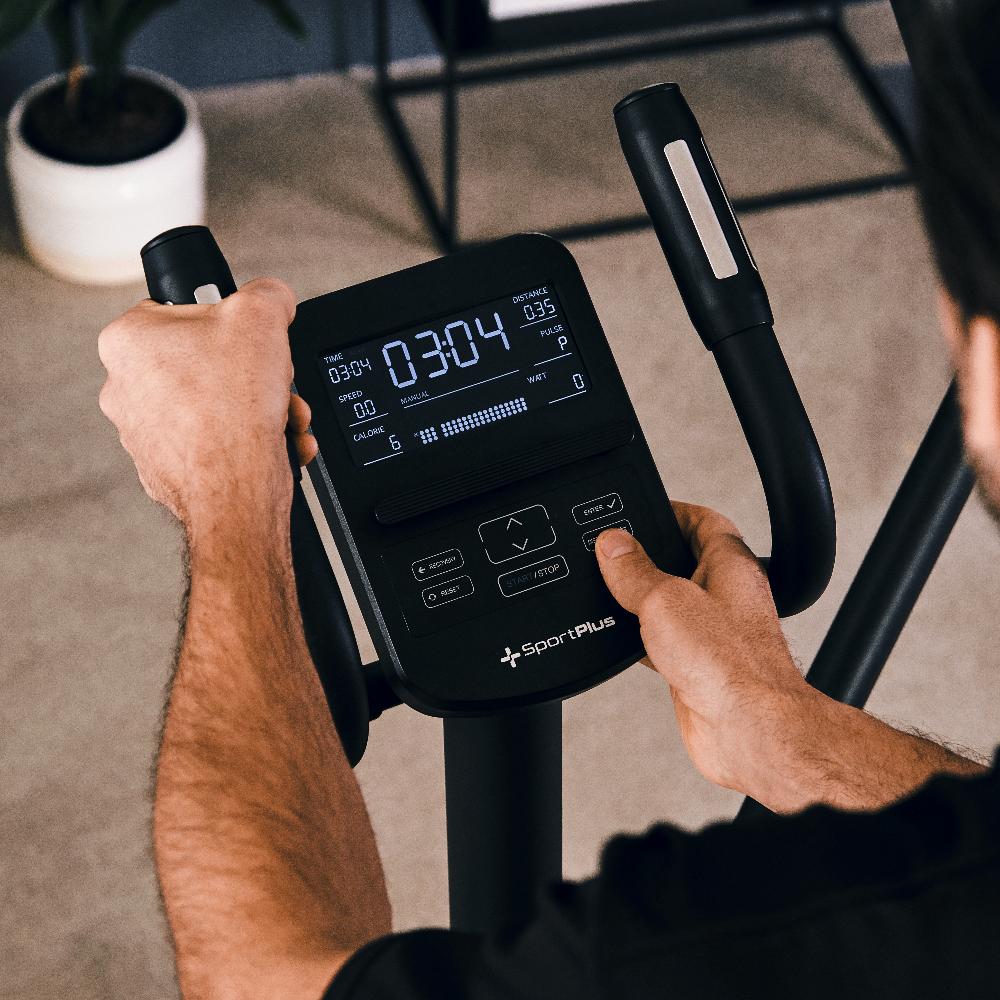
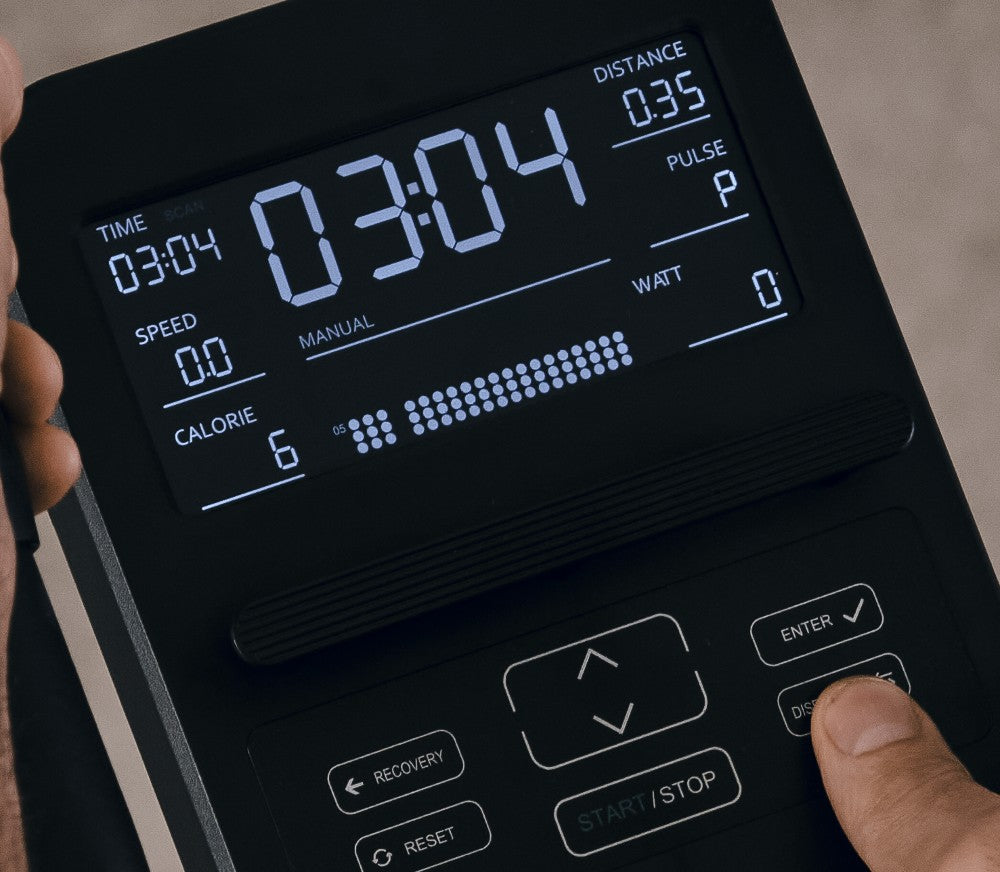
Cross trainer from SportPlus
Cross trainer with app control & 17 kg flywheel mass
Which cardio machine is right for you?
Are you still not sure whether the cross trainer is the right cardio machine for you? Take the test and find your perfect SportBuddy with us.
Are you missing the right accessories?
Are you looking for the right accessories for your cross trainer? Whether floor protection mat, chest strap or balance board, we have something for you!

Holistic endurance training at home with a cross trainer or elliptical trainer
Targeted endurance training is the right way to increase your fitness, adopt a more vital lifestyle and thus get a little closer to the figure you want.
What advantages does a cross trainer or elliptical trainer offer you?
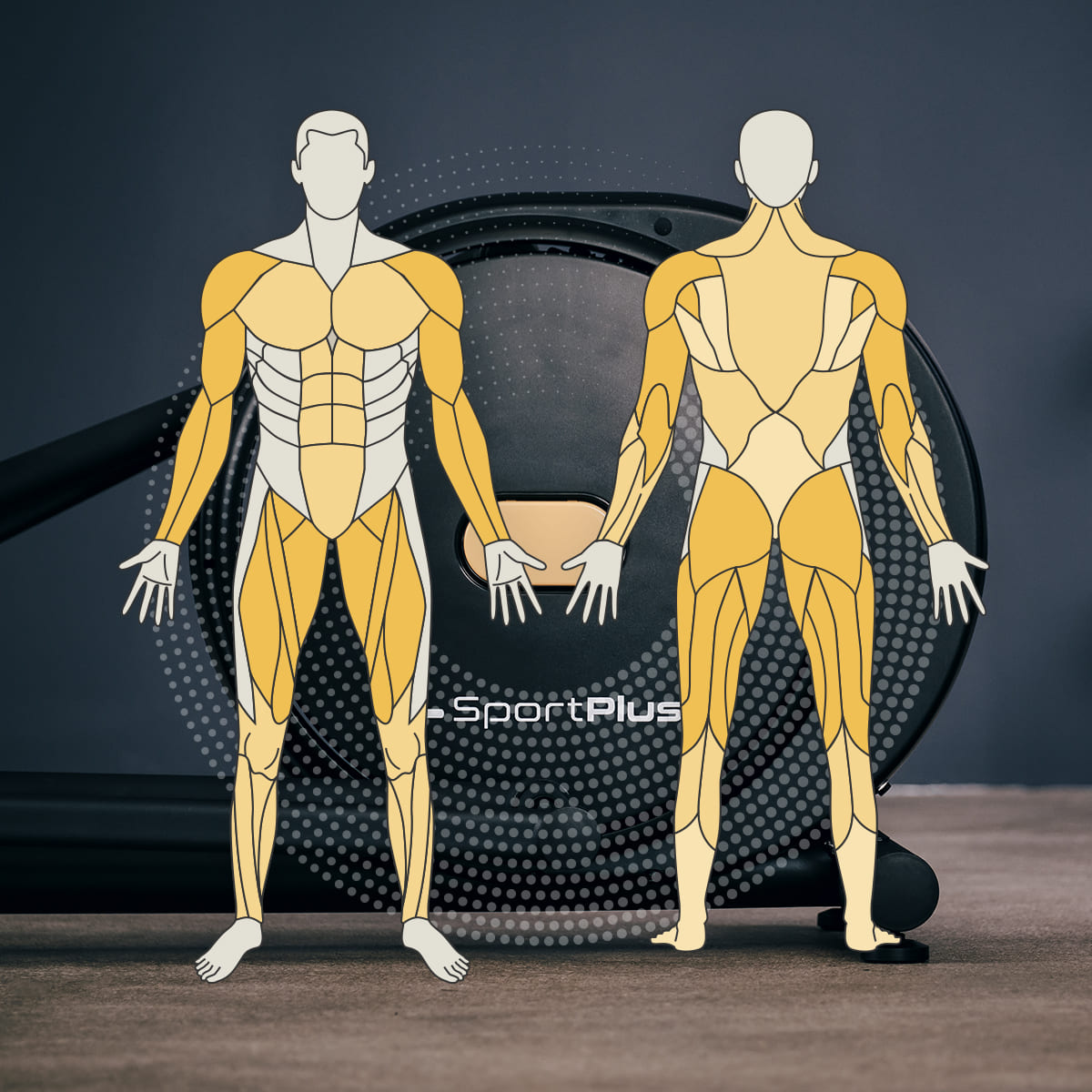
When training with a cross trainer or elliptical trainer, you can benefit from the following advantages:
- Even strain on different muscle groups
- High calorie consumption and different training modes
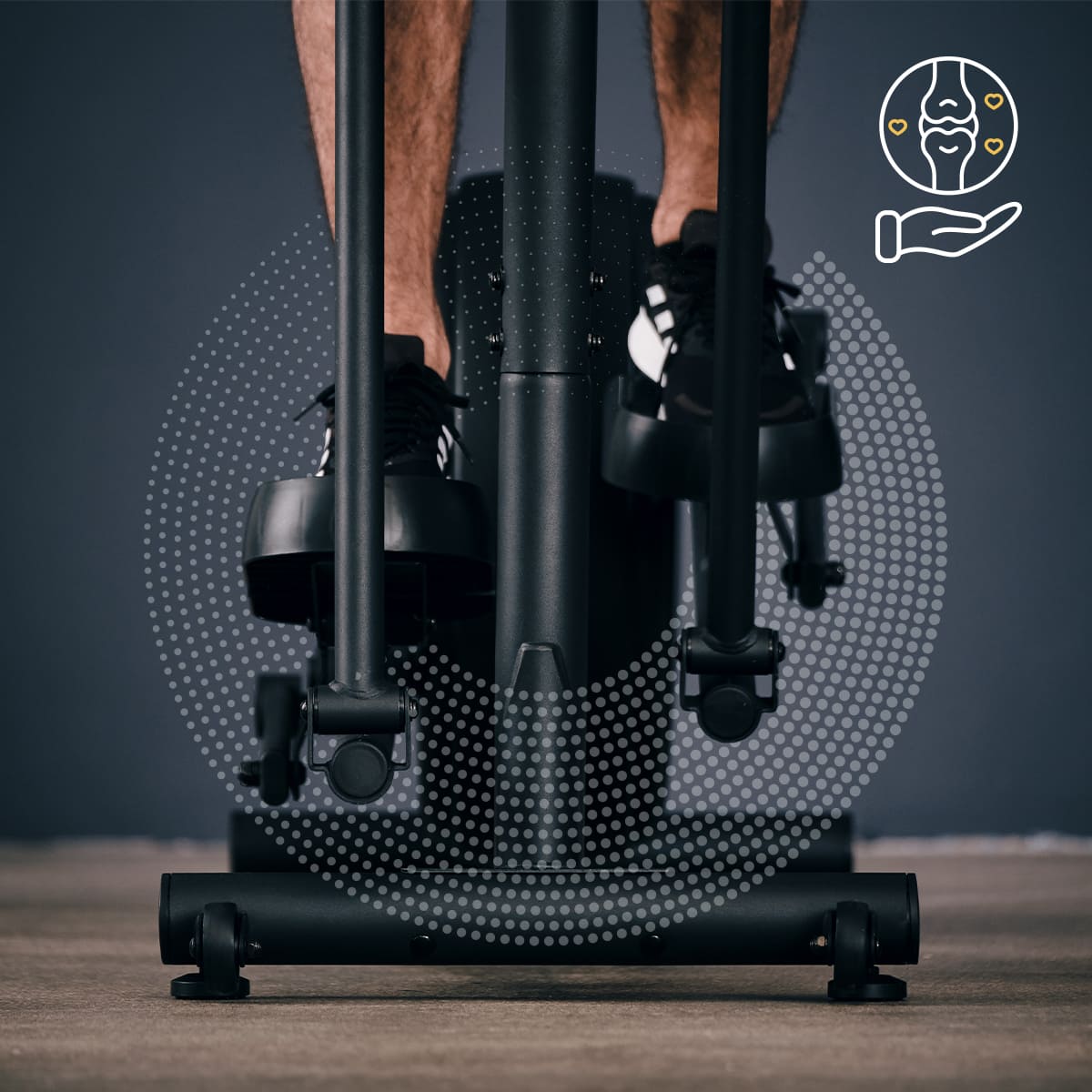
- Protecting your joints
- Possibility of running backwards
In addition, training on the cross trainer and elliptical trainer is independent of the weather. So you no longer have to put off your endurance training just because it's raining or cold.
Let's look at these benefits in detail.

What's the difference between
Cross trainer and elliptical trainer?
There aren't many differences between a cross trainer and an elliptical trainer, so the terms are often used interchangeably. However, there are some small differences in the movement sequence
find that we would like to take a closer look.

Ellipsentrainer:
Der Ellipsentrainer ermöglicht Bewegungen, die dem Gehen ähneln. Im Gegensatz zum Crosstrainer befindet sich das Schwungrad des Ellipsentrainers vor dir, sodass du eine flachere Auf- und Abwärtsbewegung ausführst. Die Bewegungen sind eher gleitend als kreisend.
Beim Training auf einem Ellipsentrainer heben sich automatisch deine Fersen etwas von den Trittflächen (Pedale) ab, was die Belastung deiner Gelenke zusätzlich reduziert. Der Bewegungsablauf ähnelt einer Ellipse (daher der Name des Geräts) und ist deutlich flacher als beim Crosstrainer. Dadurch kommt er der natürlichen Bewegung beim Laufen näher und viele empfinden es als angenehmer. In den Fitnessstudios findest du aufgrund dieser Eigenschaften hauptsächlich Ellipsentrainer. Sie sind zwar etwas kostspieliger in der Anschaffung, aber schonender für deine Gelenke und ermöglichen eine natürlichere Bewegung.
Crosstrainer:
Der Crosstrainer simuliert ähnliche Bewegungen wie beim Joggen. Das Schwungrad des Crosstrainers befindet sich im hinteren Teil des Geräts, also hinter dir. Der Bewegungsablauf ist durch eine stärkere Aufwärts- und Abwärtsbewegung gekennzeichnet. Während des gesamten Bewegungsablaufs bleiben deine Fersen fest auf den Trittflächen (Pedale). Die Bewegungsmuster sind eher kreisförmig.
Im Vergleich zum Ellipsentrainer stehst du auf einem klassischen Crosstrainer etwas breitbeiniger, da sich der Geräterahmen zwischen den Trittflächen befindet. Dadurch ist die Schrittlänge auf einem Crosstrainer deutlich kürzer als auf einem Ellipsentrainer.
Der Unterschied im Bewegungsablauf zwischen Crosstrainer und Ellipsentrainer hat jedoch keinen spürbaren Einfluss auf den Kalorienverbrauch. Letztendlich hängt es davon ab, wie wohl du dich auf dem jeweiligen Gerät fühlst.
What's the difference between
Cross trainer and cross trainer ergometer?
Ergometer is often used as a synonym for exercise bike, which is not only misleading but also wrong! Only fitness equipment that enables watt-controlled training is allowed the addition
Wear an “ergometer”. An ergometer can increase the training resistance
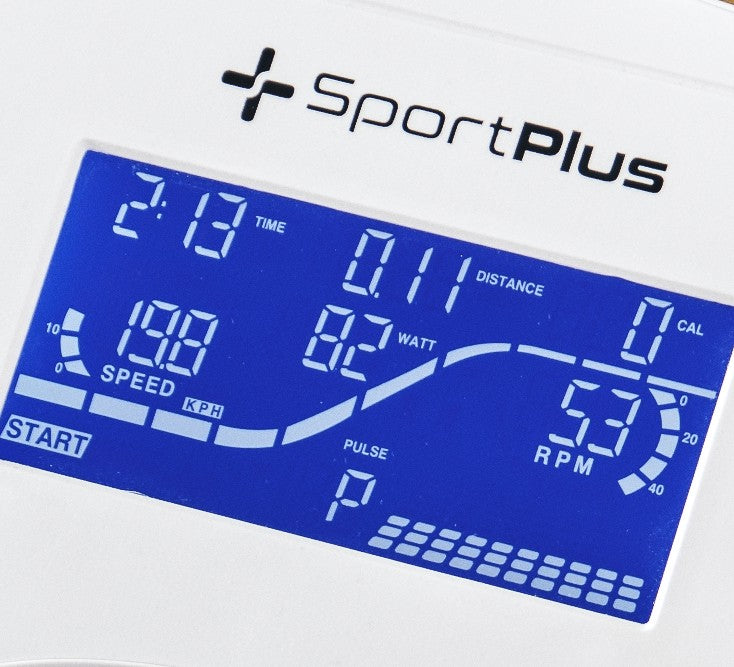
Continuously adjust a specified wattage using the magnetic brake system. Watt is a unit to measure power. With an ergometer, you can set a specific wattage specification on the training computer to ensure that you do not exceed the set performance limit.
For example, if your doctor tells you to train at 120 watts, you can only use an ergometer to ensure that you do not exceed the specified performance limit. At a
The desired watt load is always guaranteed on an ergometer, regardless of your pace. The resistance automatically adapts to the selected wattage and is controlled via the training computer.
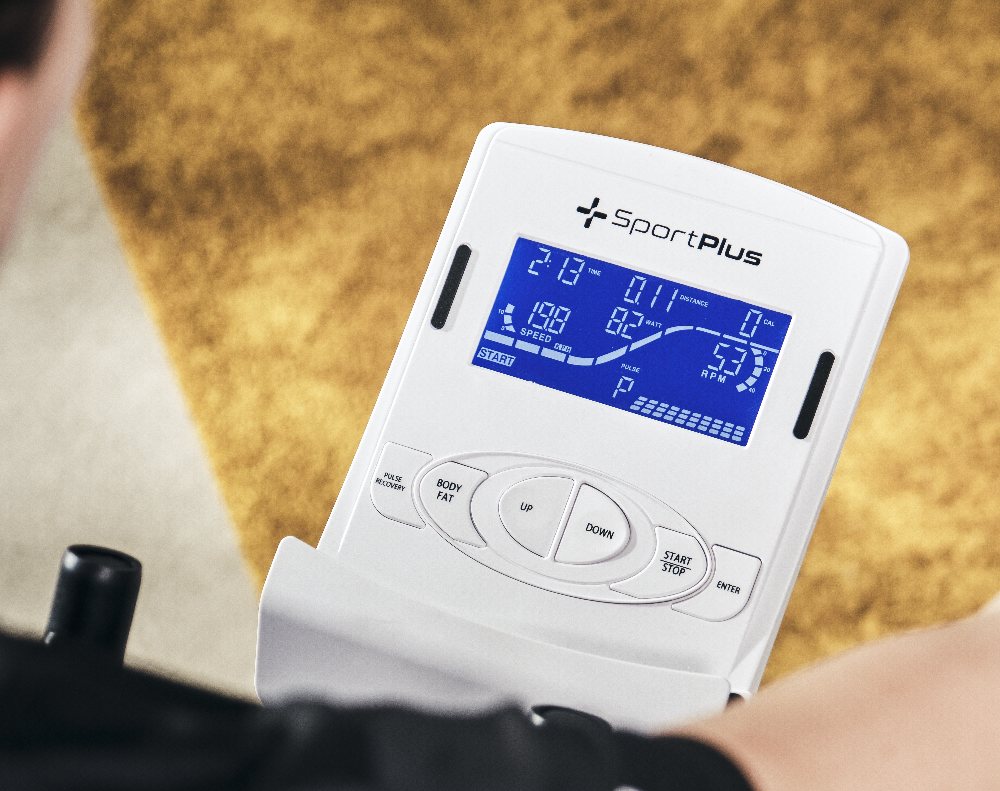
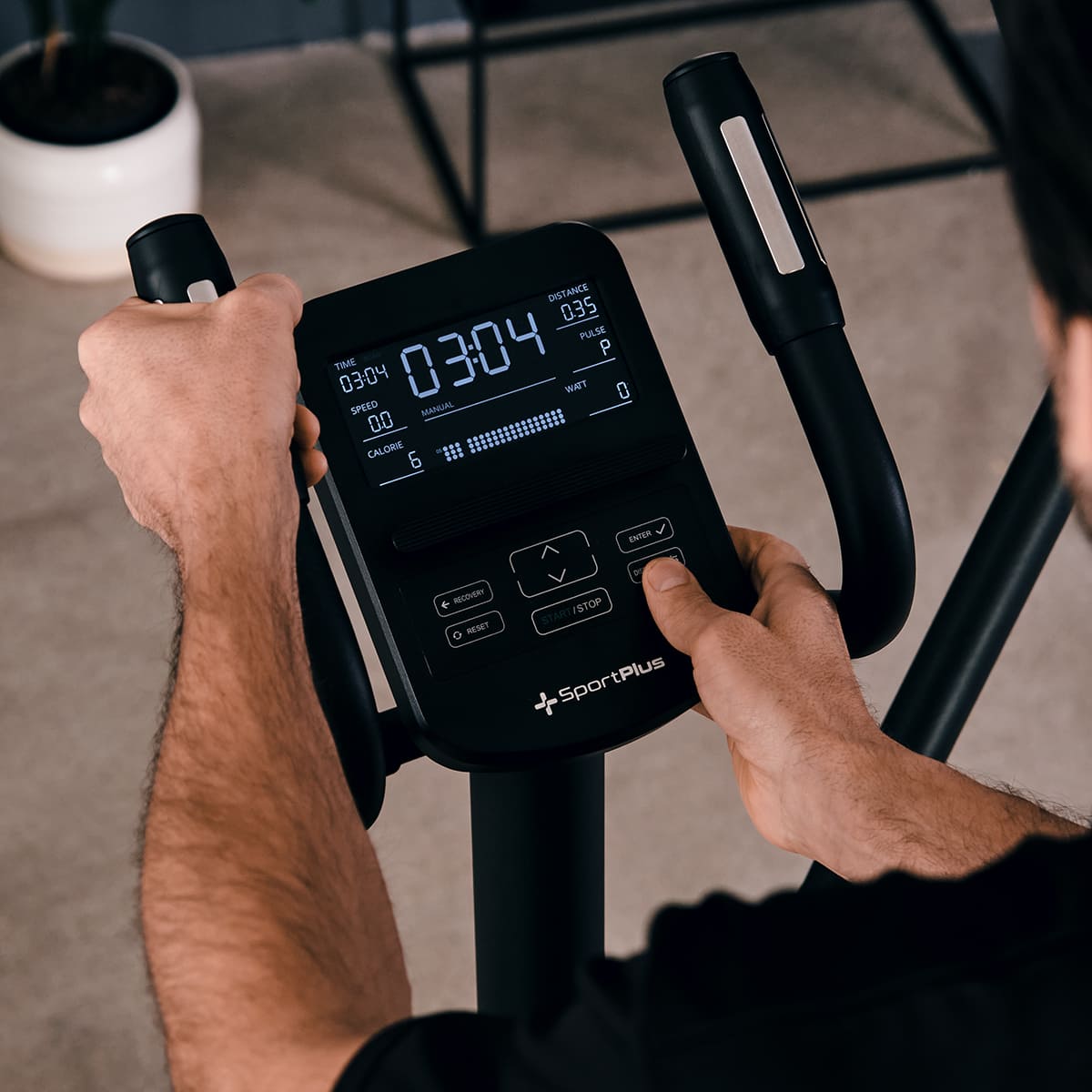


If you train more slowly, the resistance automatically increases to the set wattage. However, if you train faster, the resistance is automatically reduced so as not to exceed the specified performance limit. There are cross trainers that are called ergometers because of the possibility of watt-controlled training. However, don't be fooled when buying an elliptical exercise bike. A cross trainer that does not enable watt-controlled training is not an ergometer.
Cross trainer ergometers are particularly suitable for you if you are undergoing physiotherapeutic treatment or rehabilitation measures. That's why (almost) all physio practices and many fitness studios are equipped with ergometers.
Who is the cross trainer suitable for?
In general, cross trainers and elliptical trainers are suitable for you if you neither want to go to the gym nor run all the time. Thanks to the guided and ergonomic movement sequence, they are particularly suitable for beginners like you. It's worth purchasing if you want to lose weight or improve your endurance. If you sit a lot for work and want to train your upper body and your lung capacity, such fitness equipment is also a good choice.
Did you know already? A woman who is 170 centimeters tall and weighs 65 kilos burns around 500 calories per hour on the cross trainer with medium exertion. That's equivalent to a whole bar of chocolate. The cross trainer is a suitable companion for people who are overweight. Training that is gentle on the joints is particularly important if you are overweight. When you exercise on a treadmill with heavy weight, you risk overstressing your tendons and joints, which can lead to an increased risk of accidents.
How does a cross trainer or elliptical trainer actually work?
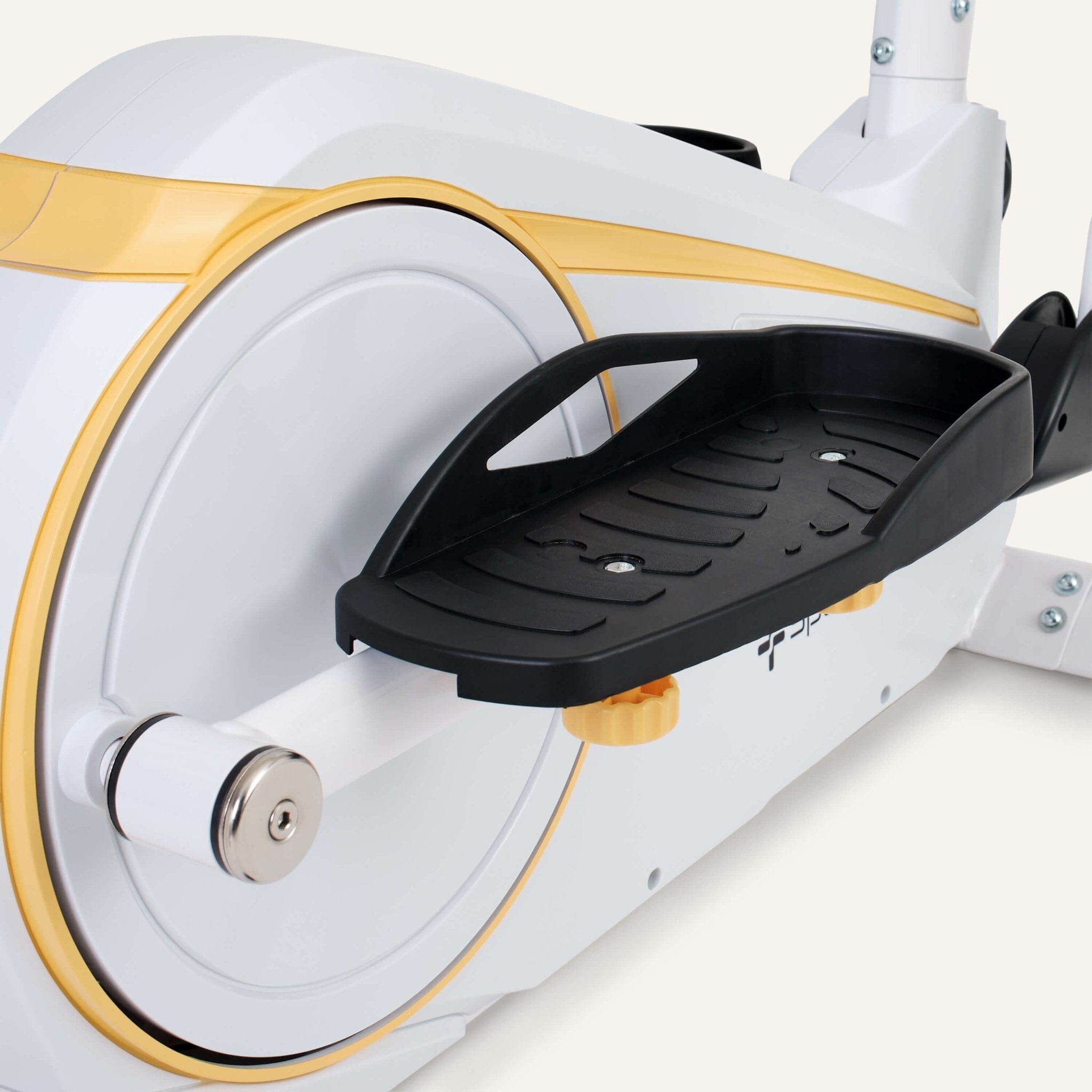
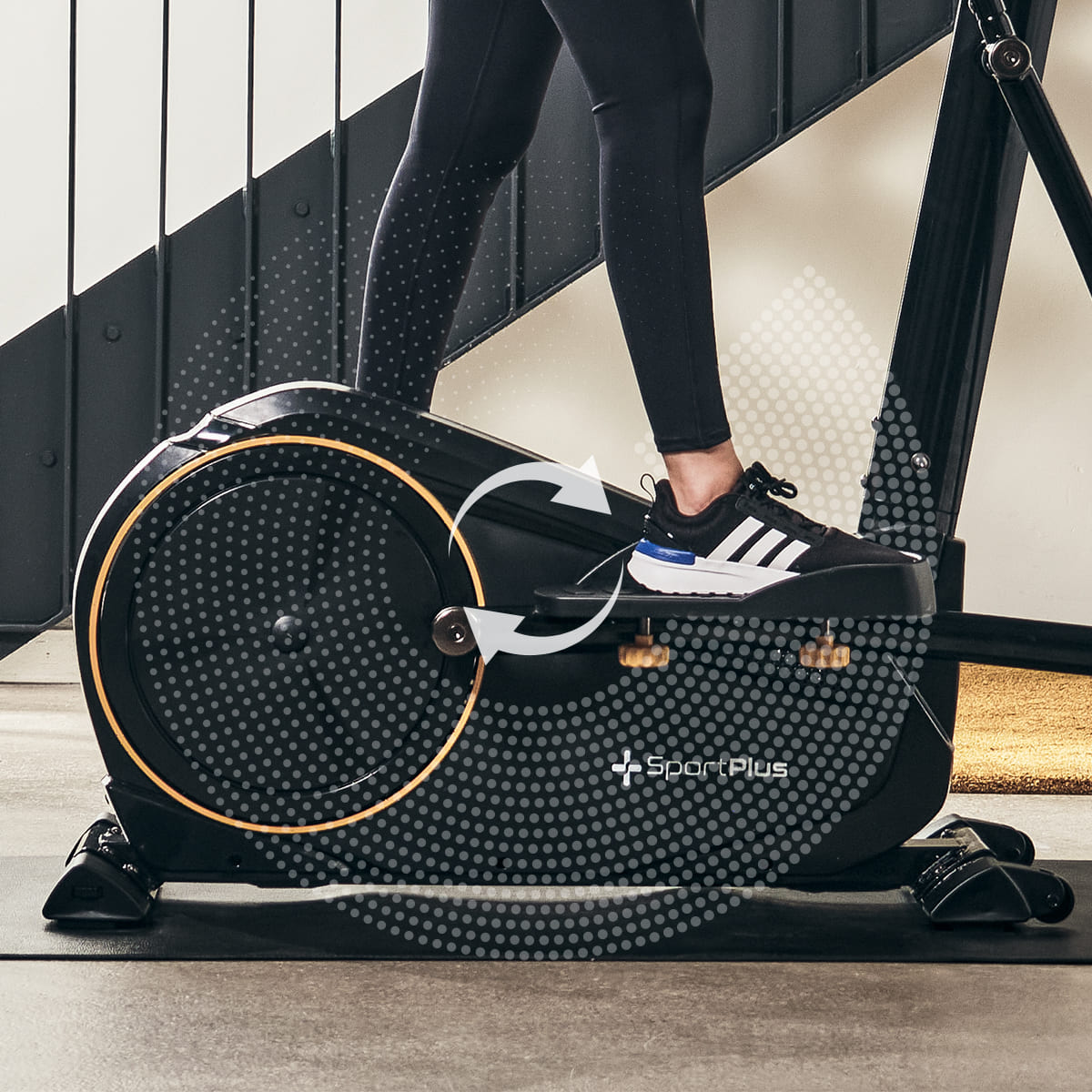
The central element of the cross and elliptical trainer is the flywheel, which is connected to the two vertical arm bars via two horizontal pedal arms. This creates a “cross” movement of the arms and legs.
- Differences in the braking system
- Differences in the flywheel/flywheel
- Differences in noise levels during operation
Below we will look at some of the points that characterize how a cross and elliptical trainer works.
Differences in the braking system
Cross trainers and elliptical trainers often use induction brakes (also: eddy current brakes) or magnetic brakes to increase resistance.
Hier sind die Unterschiede zwischen den beiden Technologien:
Magnetbremssystem
Beim Crosstrainer wird das magnetische Bremssystem mechanisch gesteuert, indem ein Permanentmagnet näher oder weiter von der Schwungmasse entfernt wird. Je näher sich das Magnetfeld an der Schwungmasse befindet, desto größer ist der Widerstand. Es findet jedoch keine direkte Berührung zwischen Magnet und Schwungmasse statt, um Verschleiß zu vermeiden. Dadurch ist der Bremsvorgang und somit der Widerstand sehr gleichmäßig, und die Last wird gut verteilt. Du kannst den gewünschten Widerstand über die Einstellung der Wattwerte am Trainingscomputer steuern.
Induktionsbremssystem
Das Induktionsbremssystem oder die Wirbelstrombremse sind ebenfalls langlebig und verschleißfrei. Denn hier berühren sich der Magnet und die Schwungscheibe nicht. Bei dieser Variante erzeugt eine elektrische Spule über einen Stromfluss ein Magnetfeld. Dies erzeugt Wirbelströme, die durch den Strom Magnetfelder erzeugen und so die Schwungmasse abbremsen.
Differences in
Flywheel and flywheel
As already mentioned, the flywheel of a cross trainer is built into the rear and is located behind you, the exerciser. That's why we refer to a cross trainer as a rear-wheel drive model. At the
On the elliptical trainer, the flywheel is located in the front part of the device, which is why we are talking about a front-wheel drive model. In the past, the weight of the flywheel, i.e. the flywheel, was considered the only quality feature. The heavier the flywheel, the more dynamic the movement. However, it is not correct to consider the weight of the flywheel in isolation. Too high a flywheel can make you feel like you're being "overtaken" by the flywheel while you exercise.
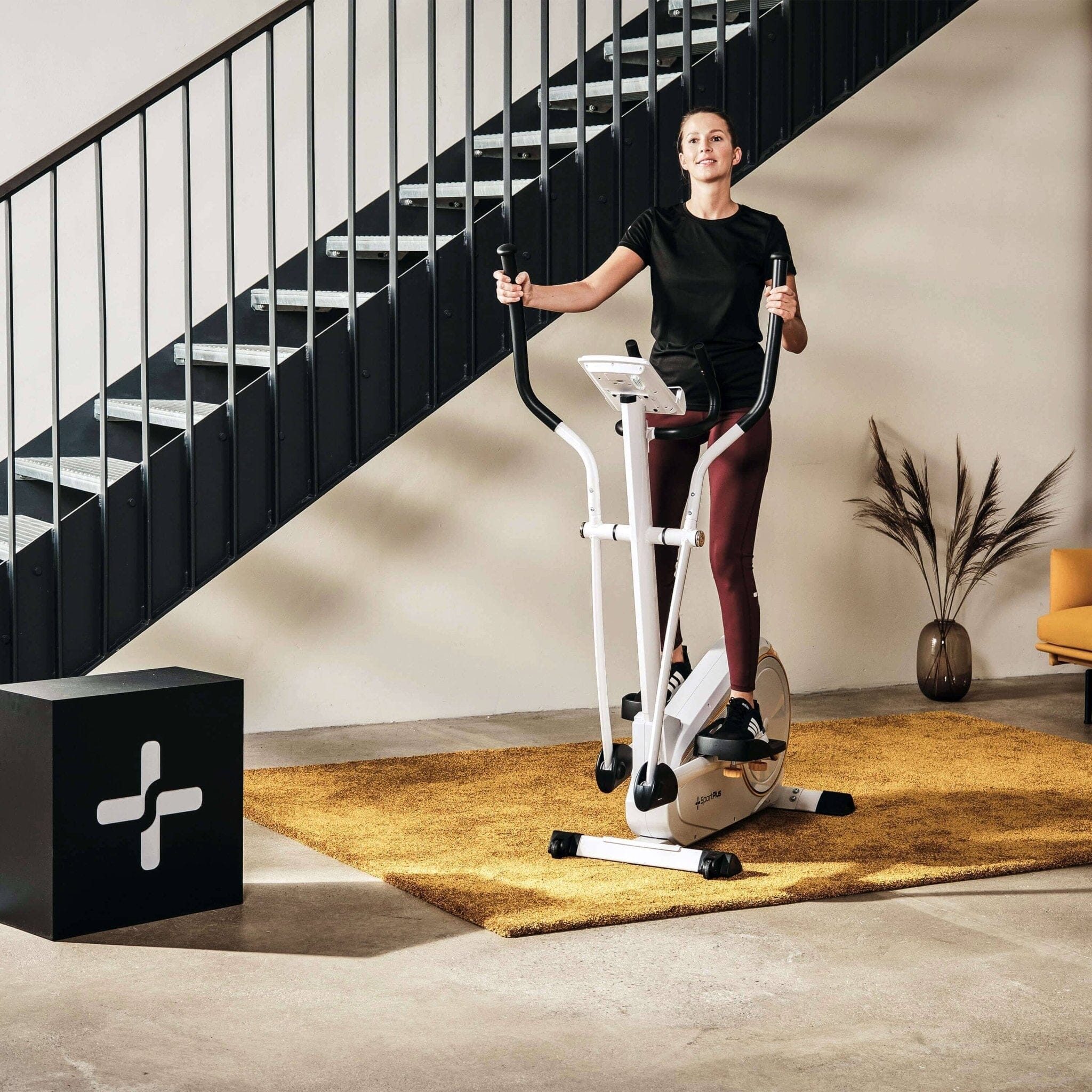


A flywheel that is too low is also counterproductive because it is not enough to overcome the so-called turning point. The turning point is the position of the pedals where one pedal reaches the highest point while the other pedal reaches the lowest point.
In this position the movement sequence is repeated every time
interrupted because there is no momentum. A sufficient flywheel ensures that this “dead point” is avoided and that the movement can continue dynamically and without interruption.
The rule of thumb is: For ambitious endurance training at home, a flywheel mass of 15 kg to 25 kg is sufficient to complete a comfortable workout!
Let us now take a closer look at the most important purchasing criteria:
Woran du auch noch beim Kauf achten solltest:
Neben den bereits erwähnten Funktionen gibt es noch weitere Faktoren, die du bei deiner Kaufentscheidung berücksichtigen solltest. Hier fassen wir sie für dich zusammen.
Dein Körpergewicht und deine Körpergröße:
Die meisten Cross- und Ellipsentrainer sind für eine Körpergröße von 2 Metern ausgelegt. Das maximale Gewicht variiert von Hersteller zu Hersteller. Es ist wichtig, dass die Tragfähigkeit des Crosstrainers zu deinem eigenen Körpergewicht passt.
Die Angabe des Maximalgewichts dient auch als objektiver Maßstab für die Qualität des Crosstrainers, da es vom TÜV und nicht vom Hersteller festgelegt wird. Je mehr Gewicht das Trainingsgerät tragen kann, desto hochwertiger sind die einzelnen Komponenten. Das betrifft insbesondere den Rahmen, das Tretlager und das Antriebssystem.
Platzbedarf und erforderliche Deckenhöhe:
Im Allgemeinen sind Crosstrainer etwas platzsparender als Ellipsentrainer, da sie kleiner sind. Die meisten Geräte sind nicht klappbar, daher musst du genügend Platz in deinem Zuhause für die Aufstellung einplanen. Neben dem Crosstrainer selbst spielt auch deine Körpergröße eine wichtige Rolle. Damit du das Training zu Hause durchführen kannst, muss das Gerät natürlich in den Raum passen.
Berechnung der Deckenhöhe: Es gibt eine grobe Formel, um die Deckenhöhe unter Berücksichtigung deiner Körpergröße zu berechnen: Körpergröße (cm) + Abstand der Pedale vom Boden (cm) = Notwendige Deckenhöhe (cm)
Achte auf hohe Qualität!:
Sportplus steht sowohl für einen ausgezeichneten Kundenservice als auch für die exzellente Qualität der Geräte. Das CE-Zeichen bestätigt, dass unsere Sportgeräte alle grundlegenden Sicherheitsanforderungen erfüllen, während das TÜV-Siegel zusätzlich bestätigt, dass das Fitnessgerät die höchsten Sicherheitsstandards erfüllt.
Sind Ersatzteile verfügbar?:
Alle Crosstrainer haben viele Verschleißteile. Je nach Anzahl der trainierenden Personen, Trainingshäufigkeit und Trainingsintensität tritt der Verschleiß früher oder später ein. Im Gegensatz zu anderen Anbietern kannst du bei SportPlus alle gängigen Ersatzteile nachbestellen. Sprich uns einfach an und wir finden eine Lösung, um dein Gerät wieder in einwandfreien Zustand zu versetzen.
Conclusion to
Cross trainers and elliptical trainers
In summary, cross trainers and elliptical trainers are great exercise machines to work on your fitness at home. They come in many different designs. In particular, there are devices that are watt-controlled and can be regulated in stages. Some cross and elliptical trainers also have practical additional functions such as pulse measurement or determining calorie consumption.